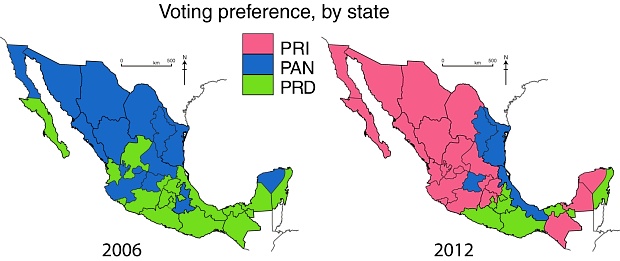
An earlier post discussed the north-south divide apparent in the 2006 presidential election. That year Felipe Calderón of PAN got the most votes in 14 of 17 northern states (blue on the map), while in 13 of 15 southern states Andrés López Obrador of PRD (green) got the most votes. Roberto Madrazo of PRI (pink) did not get the most votes in a single state.
The voting pattern changed considerably in the 2012 presidential election, but a north-south pattern still emerged. What was somewhat similar in both elections is that López Obrador of PRD retained much of his strength in southern Mexico. In both elections, PRD got most votes in seven southern states: Federal District, Morelos, Tlaxcala, Guerrero, Oaxaca, Tabasco and Quintana Roo. In 2012 PRD won in one other state, Puebla, which favored PAN in the 2006 election. Six southern states switched from PRD to PRI: Michoacán, México, Hidalgo, Veracruz, Chiapas and Campeche. Puebla switched from PAN to PRD, while Yucatán went from PAN to PRI.
In the north, the pattern changed completely with the PRI replacing PAN as the highest presidential vote-getter. A total of 11 northern states switched from PAN to PRI: Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Sinaloa, Durango, Aguascalientes, San Luis Potosí, Jalisco, Colima and Querétaro. In 10 of these states PAN came second while PRD took second place in Baja California. In 2012 PAN got most votes in only three states–Nuevo León, Tamaulipas and Guanajuato–compared to 16 in 2006.
PRD appears to have lost much of its relatively weak following in northern Mexico. The three northern states PRD won in 2006 all switched to PRI: Baja California Sur, Nayarit and Zacatecas. In 2012, PRD could only manage second place finishes in three states: Baja California, Nayarit and Zacatecas.
While the north-south pattern is still somewhat apparent, the main pattern of the 2012 presidential election is a strong victory for PRI candidate Enrique Pena Nieto. PRI was victorious in 22 of 32 states and came in second in the other ten.
However, PRI fell just short of controlling Mexico’s Congress so it will need support from some other parties to pass needed legislation and reforms. Together with minority coalition partner PVEM (Mexico’s Green Party), PRI won 240 of the 500 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 62 of the 128 seats in the Senate. On the other hand, PRI has recently indicated support for many reforms similar to those previously proposed by PAN. This implies that needed reforms may have a decent chance of passing.
Further reading, with state by state analysis:
- Geographical diversity in Mexico’s presidential elections [Terra Ignota blog]
Related posts:
One Response to “Mexico’s north-south political divide persists, albeit with minor changes”
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.
I think the latest information indicates that PRI got slightly more presidential votes in Veracruz than PAN.