What happens if or when Mexico City needs more water than it is using at present? There are several options, depending on whether authorities choose to modify demand, supply, or both in order to improve the future situation.
In terms of managing (reducing) demand, conservation measures are one possibility. Changing consumer habits may require not only educational programs, but also usage tariffs that reflect the true costs of supply, and that encourage consumers to install water-saving devices and introduce water-saving practices in their daily lives. Demand would also be reduced if less water was lost through leakage. As mentioned in a previous post, in 2009, the National Water Commission (Conagua) estimated that a staggering 40% of potable water nationwide was being lost through leaks in city and municipal systems, with a further 20% not properly accounted for due to billing errors and clandestine connections.
Managing demand may be easier to achieve than managing supply, given that recent efforts to increase supply have met with concerted opposition from environmentalists and the people living in the areas from which water would be transferred to the city. In the last half of the twentieth century, while one political party (PRI) held power, it was possible for politicians to largely ignore the conflicts resulting from inter-basin transfers, arguing that their “solutions” served a national need. Now that local, state and federal politics are more contested, that approach is potential political suicide.
From a political perspective, the most acceptable source of additional water for Mexico City would probably be the recently identified deep aquifer described in Mexico’s major cities confront serious water supply issues. However, that discovery requires further research before its maximum sustainable yield can be determined or it can be brought into service.
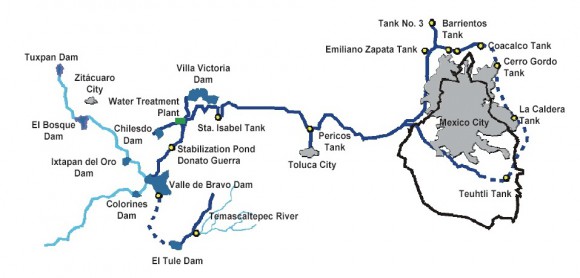
Less politically acceptable are the various proposals to bring water from elsewhere to satisfy the thirst of Mexico City. One of the most frequently voiced suggestions is to add a fourth phase to the Cutzamala scheme (see Where does Mexico City get its water from?) to increase the amount of water it supplies by more than 25% to 24 m³/s. In addition, the plan would provide treatment for 42 m3/s of wastewater. This fourth phase, known as the Temascaltepec project (see map), would require the construction of a 120-meter-high, 740-meter-long dam on the Temascaltepec River to create a reservoir with a capacity of 65 million m³.
Aqueducts and a 19-km-long tunnel would carry the water to the Valle de Bravo reservoir. The estimated cost would be $500 million. The Temascaltepec project is opposed by environmentalists and locals and is not likely to get under way any time soon. The residents of the villages near the proposed dam site are afraid that the project would cause their local springs to dry up and would adversely impact their farming of maize, sugar cane, banana, tomato, melon and peas.
To the south of Mexico City, an entirely different proposal is to bring water from the Amacuzac, Tecolutla and Atoyac Rivers, by damming the Amacuzac River, creating a 67 km2 reservoir (between the states of Morelos, Guerrero and Puebla) capable of storing 4,000 million cubic meters. Supplying Mexico City would require a 160 km long aqueduct, and would involve pumping water to a height of 1825 meters, requiring up to 5% of Mexico’s annual national electricity production. On the plus side, this could reduce the future abstraction of groundwater by as much as 50 m³/s.
Related posts:
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.