Much of Mexico is currently affected by some degree of drought (see map below). The National Meteorological Service (SMN) reports that September was one of the driest months in some 70 years. All the signs suggest this is the worst year for drought since 1941. The worst affected states are Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Durango, Nuevo León and Zacatecas. (Paradoxically, some parts of southern Mexico, especially in the states of Oaxaca and Tabasco, have experienced serious flooding in recent months).
In the drought zones, emergency programs are getting underway to provide temporary work for many rural dwellers and to supply potable water to the worst affected settlements. In addition to crop losses, up to one million head of cattle will have been put down by year-end in northern states as a direct result of the drought, since farmers do not have sufficient fodder available to feed them as usual.
While some cattle have been exported to the USA, local meat prices will be driven down by the increase in supply, making many farmer’s livelihoods even more precarious. Many farmers will need federal assistance to overcome this latest crisis.
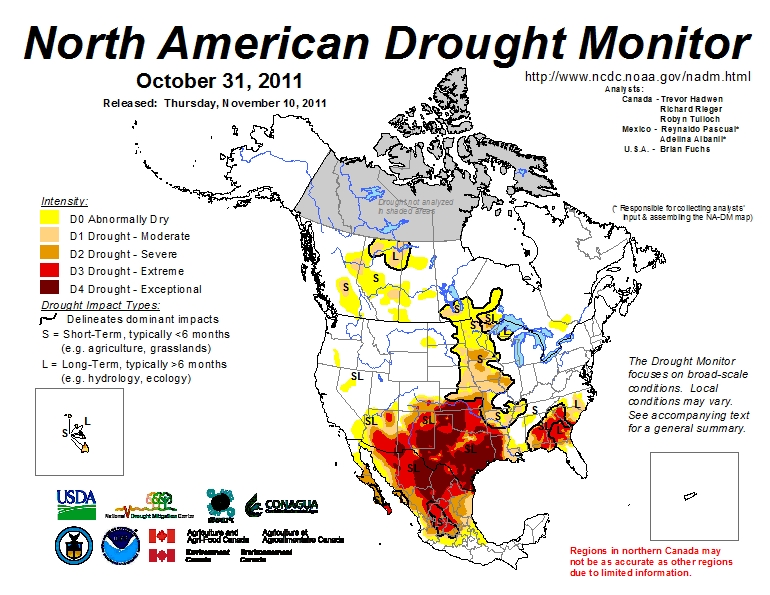
- Areas suffering from short-term and long-term drought, October 2011. Click map to enlarge
Durango faces the worst drought for 100 years
In Durango, water has been provided to 32,691 residents in 10 municipalities, with another 36 municipalities to be supplied in the current phase of emergency assistance. Officials in Durango say it is the state’s worst drought for 100 years, with most larger reservoirs in the state now holding between 20% and 40% of their capacity; one reservoir is already down to less than 10% of its.
Irregular rains over the past few months have done little to replenish reservoirs, leaving farmers in despair. The long-range forecast does not appear to offer them much consolation, with the drought expected to last well into next year.
By mid-September, some parts of Durango had received less than 140 mm of precipitation so far ths year, well below the 425 mm registered for the same period in 2010. The only hope for local farmers appears to be if late season hurricanes bring far more rain than expected to this region.
The drought news from other states
In Chihuahua, 589 tankers have delivered water to settlements housing 62,000 in 15 different municipalities: Guazapares, Janos, Manuel Benavides, Morelos, Moris, Ocampo, Ojinaga, Urique, Uruachi, Aldama, Balleza, Bocoyna, Guachochi, Guadalupe and Calvo.
In Zacatecas, a “state of emergency” has been declared for 52 of the state’s 58 municipalities. More than 150 communities are seriously affected, especially smaller communities in the municipalities of Fresnillo, Jerez, Guadalupe, Tlaltenango, Nochistlán, Atolinga, Villa de Cos, Genaro Codina and Teúl de Gonzalez Ortega.
Drought has affected 288,000 hectares of rain-fed crops in Guanajuato. The greatest losses are of corn, beans, wheat, sorghum and other grains, with the worst-hit areas located in the northern part of the state. More than a million liters of potable water have been supplied to 18,000 inhabitants living in 133 settlements in the state, located in the municipalities of Atarjea, Doctor Mora, San Diego de la Unión, San Felipe, Santa Catarina, Tierra Blanca, Victoria and Xichú.
Horticulturalists in Sinaloa growing vegetables, grains and fruit for export want 30 million dollars in emergency funds to restore irrigation to 700,000 hectares of productive land. More than 200,000 seasonal jobs are at risk.
Related post:
- Mexico, USA and Canada cooperate to produce monthly drought maps
- Mexico’s freshwater aquifers: undervalued and overexploited
- The availability of water in Mexico
Mexico’s water resources and water-related issues are the subject of chapters 6 and 7 of Geo-Mexico: the geography and dynamics of modern Mexico. Ask your library to buy a copy of this handy reference guide to all aspects of Mexico’s geography today! Better yet, order your own copy…
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.