This year’s drought – see Many states in Mexico badly affected by drought – is now widely viewed as the worst to occur since modern record-keeping for precipitation began about 80 years ago.
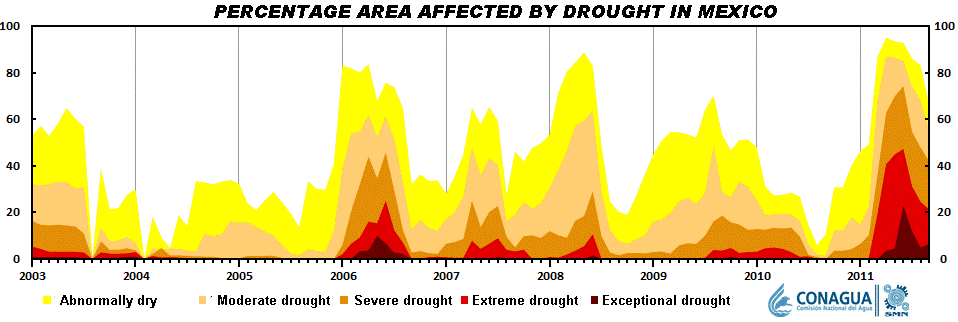
Short-term droughts are not unusual in Mexico. As the graph shows, there is a clear cyclical pattern to the timing of short-term droughts in Mexico. This is because most of the country receives almost all its annual precipitation in just a few months, from May or June (depending on precise location) to September-October.
The scale of the current drought is readily apparent from the graph. This year, far more of the country is affected, and the level of drought is far more severe.
The drought is having numerous adverse impacts
It is already having an effect on food prices. Several of the basic foodstuffs making up Mexico’s basic basket of goods for economic indices such as the inflation index, have risen sharply in price in recent months. A shortage of corn has led to a 70% increase in imports of yellow corn from the USA.
Incredibly, Mexico, the home of corn, is now the world’s second largest importer. Corn, as we have noted in previous posts, is a vital ingredient in Mexican cuisine, and is particularly important in the southern half of the country, especially in the more rural and indigenous areas. The shortage of corn has led to a rise in the price of tortillas, a dietary staple in almost all of the country. Tortilla prices have risen up to 18%, many times Mexico’s overall inflation rate of about 3.5%.
The production of chiles, another staple of the Mexican diet, has also fallen due to the drought, by an estimated 40%. In Zacatecas, that state’s 2,500 chile-growers will have produced 120,000 tons of green chile and 62,150 tons of dried chile this year, even though they have only been able to harvest chiles twice this year, rather than the normal four times. The state is the leading source of dried chile in Mexico. The area cultivated for chiles in Zacatecas has also fallen this year, to 31,300 hectares. The decrease in production has had a direct impact on the number of harvesting jobs available, since each hectare of chile cultivation usually means 150 seasonal jobs. The production shortage for chiles will be offset by more imports from Peru and China.
At latest count, 770 municipalities are now suffering from drought, and at least 2.5 million people in 1500 communities are left with insufficient drinking water. In the state of Durango alone, more than one million people are currently experiencing extreme drought, and 149 communities are completely without drinking water.
The long-term outlook is not favorable for these areas since climate change is expected to increase both the frequency and severity of droughts over the next twenty to thirty years.
Related posts:
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.