The remote mountains and plateaus where the states of Jalisco, Nayarit and Zacatecas all meet is home to some 18,000 Huichol Indians, as well as their close cousins, the Cora. The Huichol (Wixárika = “the healers” in their own language) live in scattered, extended family, settlements (ranchos) and rely entirely on oral tradition. They are intensely religious, and see their time-honored responsiblity as protecting nature’s creations. Their shamen perform elaborate ceremonies to a pantheon of gods to ensure bountiful crops, health and prosperity, as well as to preserve nature and heal the Earth.
The center of the Huichol world – Tee’kata (see map) – coincides with the village of Santa Catarina in the Huichol heartland. Central to some Huichol ceremonies is peyote, an hallucinogenic cactus, obtained from an annual pilgrimage eastwards to the sacred land of Wirikuta, near Real de Catorce in San Luis Potosí. The pilgrimage is an 800 km (500 mile) round trip. Peyote (Lophophora williamsii) is called jicuri by the Huichol.
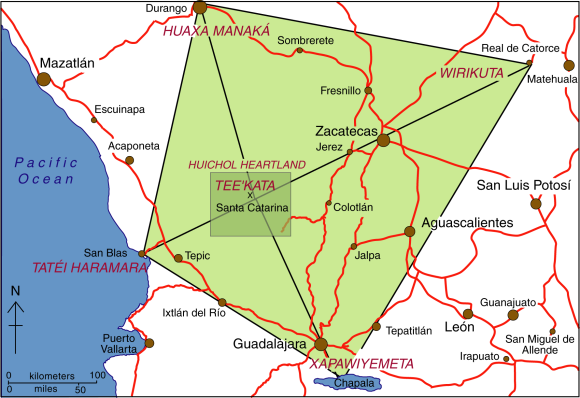
The sacred geography of Mexico’s Huichol Indians. Credit: Tony Burton/Geo-Mexico; all rights reserved.
Equally important points in the Huichol cosmos lie to the north, west and south:
- north: Huaxa Manaká = the mountain of Cerro Gordo in Durango
- west: Tatéi Haramara = the Isla del Rey, an island near San Blas
- south: Xapawiyemeta = Scorpion Island (Isla de los Alacranes) in Lake Chapala
The sacred geography of the Huichol (shown by the rhombus on the map) echoes the significance they attach to the number 5. They view the world as having five regions, corresponding to five mothers (one under the earth and the other four at cardinal points). They believe that the sun is carried through the universe by five serpents. The flowers of their sacred peyote come in five colors, as do their cobs of corn (Blue, white, reddish purple, yellow, multicolor). The Huichol have different terms for the five colors of corn, which are closely associated with the five main points of their cosmos:
- yuawime – blue – south
- tuxame – white- north
- ta+lawime – purple – west
- taxawime – yellow – east
- tsayule – multicolor – center
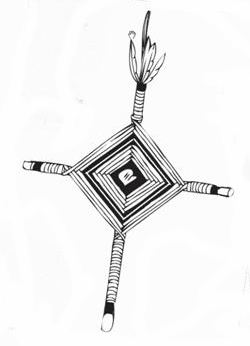 Every rhombus has four corner points and a center. Their traditional yarn crosses (often mistakenly referred to as “God’s Eyes”) are made by wrapping colored yarn around two twigs to form a rhombus of color. Most yarn crosses use several different colors. Compound yarn crosses are made by adding small yarn crosses at each end of the two main supporting twigs, giving five crosses (eyes) in total. Huichol fathers will make a simple yarn cross when a child is born, adding additional crosses annually until the yarn cross is considered complete. This, of course, is assuming that the child survives, given that infant mortality among the Huichol is very high.
Every rhombus has four corner points and a center. Their traditional yarn crosses (often mistakenly referred to as “God’s Eyes”) are made by wrapping colored yarn around two twigs to form a rhombus of color. Most yarn crosses use several different colors. Compound yarn crosses are made by adding small yarn crosses at each end of the two main supporting twigs, giving five crosses (eyes) in total. Huichol fathers will make a simple yarn cross when a child is born, adding additional crosses annually until the yarn cross is considered complete. This, of course, is assuming that the child survives, given that infant mortality among the Huichol is very high.
The colors used in Huichol artwork also carry lots of symbolism. For example, blue is taken to mean water or rain and associated with Lake Chapala to the south. Black symbolizes death and is linked to the Pacific Ocean in the west. Red, the color for mother, is usually reserved for sacred places such as Wirikuta in the east. White (clouds) is associated with the north.
Related posts:
- The geography of the Huichol Indians: the regional setting
- The geography of the Huichol Indians: traditional lifestyles and settlement patterns
- The geography of the Huichol Indians: cultural change
- The transformation of Real de Catorce from ghost town to film set and Magic Town
- The geography of languages in Mexico: Spanish and 62 indigenous languages
- An overview of Mexico’s indigenous peoples
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.