Wildlife groups from around the world are urging the Mexican government to take urgent action to prevent the extinction of the “little sea cow”, the world’s smallest porpoise, known in Spanish as the vaquita marina, currently the most endangered cetacean in the world.
This particular porpoise is only found in the upper sections of the Sea of Cortés (Gulf of California), and fewer than 100 are thought to exist.
Scientists say that gill-net fishing must be eliminated in the little sea cow’s native habitat for its population to have any hope of recovering to a sustainable level. Mature females will usually only give birth to one calf every two years. Even with a total ban, it would therefore take several years for natural increase to boost the population. In the port of El Golfo de Santa Clara studies have suggested that gillnet fishing is responsible for approximately 39 vaquita deaths a year.
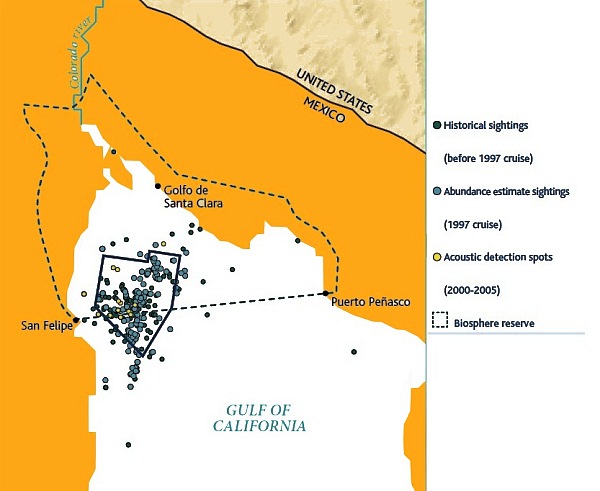
Map of sightings and acoustic detection spots. Adapted from North American Conservation Action Plan for the vaquita
According to Jo Tuckman, writing in The Guardian, environmental groups blame the decline of the popoise population on a “booming illegal trade in the totoaba fish (mistakenly called “toboada” in The Guardian), driven by Chinese demand for its swim bladder, which is believed to have medicinal properties.” Chinese fishermen are alleged to have overfished a similar fish in their own waters, leading to a sharp increase in demand for imports of totoaba. Fishermen in the Sea of Cortés are reported to have been offered more than $4,000 for the single bladder (which weighs 500 grams) of a mature fish.
There have been numerous reported instances of illegal cross-border trade in totoaba bladders, including, Man Admits to Smuggling Swim Bladders of Endangered Fish. The fish has been listed as “endangered” since 1979 under the U.S. Endangered Species Act. Between February and May 2013, border inspectors in Calexico, Arizona, seized the swim bladders of more than 500 endangered Totoaba.
In 2008, Mexico, the USA and Canada launched the North American Conservation Action Plan (NACAP) for the vaquita, under the jurisdiction of the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC), a NAFTA environmental organization. Mexico has also established a program known as PACE-VAQUITA, which compensates fishermen who choose one of three alternatives to commercial fishing: rent-out (payments to avoid fishing in specific areas which are known to have resident vaquitas), switch-out (compensation and inducement to switch technology to vaquita-safe methods), and buy-out (compensation for permanently relinquishing their fishing permits and gear).
Clearly, these efforts have not yet paid off and more stringent controls and enforcement are desperately needed if the vaquita marina is to be brought back from the brink of extinction.
Update (31 December 2014):
“The Mexican federal government has recently proposed a US $37 million compensation plan that would ban gillnet fishing in waters inhabited by the world’s most endangered mammal species.” (Mexico News Daily, 27 Dec 2014)
Want to read more?
Related posts:
- Mexico imposes seasonal ban on all shark fishing
- Overfishing in Mexico’s Sea of Cortés (Gulf of California)
- How sustainable is commercial fishing in northwest Mexico?
- Mexico’s pearl collection industry: from boom to bust in less than 100 years
- The extraordinary ecological recovery of Mexico’s Cabo Pulmo Marine Park
- Colorado River delta returning to life
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.