This post presents a short case study of the dramatic ecocide in the Hurtado Reservoir in Jalisco a week ago that resulted in the sudden death of between 200 and 500 tons of fish.
What?
- The ecocide killed between 200 and 500 tons of fish
- 30 local residents were affected by gastrointestinal problems
- 15 of them required treatment in local health centers
Where?
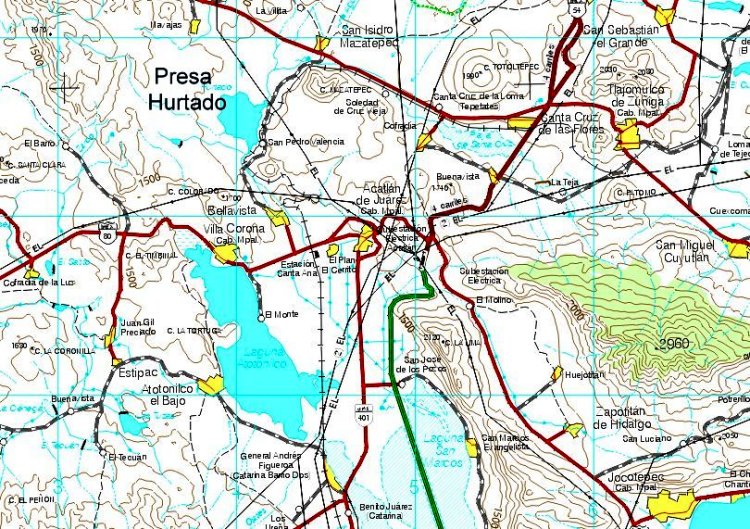
The ecocide occurred in the Hurtado Reservoir (Presa del Hurtado, aka the Valencia Dam) in Jalisco, mid-way between the villages of San Isidro Mazatepec and Bellavista, the location of a sugarcane mill (see map). The reservoir can hold up to 8,000,000 cubic meters of water. The two municipalities involved are Acatlán de Juárez and Tlajomulco de Zúñiga. The most affected community is the small village of San Pedro Valencia (about 300 inhabitants),
When?
The first reports were made on 25 June when a local government official in San Pedro de Valencia, in the municipality of Acatlán de Juárez, reported to state environmental protection officials that the water in the Hurtado Reservoir was contaminated with something smelling like molasses. Within 48 hours, officials had identified the source, and had conducted a formal inspection, reporting that the water was dark brown in color and contaminated with molasses.
Why?
According to press reports, an unlicensed firm in nearby Potrero los Charros was using molasses (a by-product of sugarcane mills) as an ingredient to make cattle food. Some of the molasses (melaza) was dumped into the San Antonio stream which carried them into the reservoir.
The problem arose because molasses have a very high biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). This means that they require large amounts of oxygen as they decompose. In this case, they required more oxygen than was available in the water in the reservoir, reducing the water’s dissolved oxygen content, effectively depriving all aquatic life of oxygen. While final results are pending, the fish are believed to have died of oxygen starvation.
Effects
- The local fishing cooperative of the Hurtado Reservoir has agreed to accept a moratorium on catching, selling or consuming local fish. The fishermen normally catch and market about 100 kg of fish a day.
- Health services are offering vaccinations to local residents and all those involved in the environmental clean-up.
- 18 local restaurants are closed until further notice. When they reopen, they will likely have to purchase fish from further away (eg the fish market in Guadalajara) at a higher price than they previously paid for local fish
- About 100 fish traders in nearby towns (including Tala, Acatlán de Juárez and Villa Corona) have lost a source of income.
Responses
- Within 48 hours of the first report, authorities had ordered the business responsible for the pollution to take immediate remedial action. Meanwhile, authorities began to clean up the dead fish. The fish are being buried in a 30 meter by 2 meter trench about one km away from the lake.
- Federal officials from the National Water Commission and the Environmental Secretariat were quickly on the scene; they promised access to federal financial assistance.
- Most of the clean up was carried out by about 100 local fishermen and volunteers, including firefighters.
- State health officials have closed the 18 small fish restaurants near the lake until further notice
- Local officials are also cleaning up the storage area, using tanker trucks to remove an additional 8,000 tons of molasses for appropriate disposal elsewhere.
- The municipality of Tlajomulco has issued the owner of the company with a fine of about 1.5 million pesos ($120,000) and further legal action is underway.
Remediation
- Environmental expert Gualberto Limón Macías estimates it will take between two and four years to rehabilitate the reservoir. The priority is to re-oxygenate the water, possibly using solar-powered pumps, and seed the reservoir with young fish.
- The University of Guadalajara has promised to arrange for a team of experts to provide specialist advice about how best to rehabilitate the lake.
Related posts:
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.