We have repeatedly questioned the long-term wisdom of large-scale tourist developments along Mexico’s coastline. See, for example:
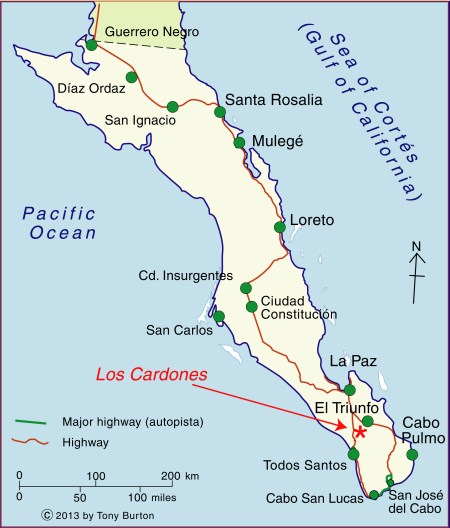
The good news, in June 2012, was that it looked as if the conflict at Cabo Pulmo, in Baja California Sur, had been resolved in favor of protecting the environment:
Unfortunately, land developers won’t take “No” for an answer. Immediately after its “cancellation”, the Cabo Cortés project was renamed Los Pericúes and relaunched, with few if any differences from the original version. Two years on, the project has been taken over by a new consortium of developers and renamed “Cabo Dorado”. Some changes have been made along the way, and Cabo Dorado no longer includes a marina or desalination plant, and its plans appear to have a lower building density.
There are still some legitimate concerns about the long-term impact of such a project in this area, so kudos to Carolina Herrera (Latin America Advocate of the Natural Resources Defense Council in Washington DC) for her impassioned plea calling for Cabo Pulmo to be protected from the latest incarnation of this long-proposed tourist megaproject.
The project is located immediately north of the Cabo Pulmo Marine Park, which over its 19 year lifespan has proven to be hugely successful in conservation terms (The extraordinary ecological recovery of Mexico’s Cabo Pulmo Marine Park), while providing local people with the opportunity to offer a variety of alternative forms of low impact tourism. The site of the Cabo Dorado project site is home to 26 “at risk” species, including endemic plants and endangered sea turtles.
Cabo Dorado is a 3.6-bilion-dollar joint investment by La Rivera Desarrollos BCS, a joint venture of Glorious Earth Group (USA) and Beijing Sansong International Trade Group (China), together with China State Construction Engineering Corporation.
The project is for the construction of a new “ecotourist city” on 3770 hectares (9317 acres) of land. Slightly more than two-thirds of this area will be retained as a “conservation reserve”.
The master plan for the developed third includes:
- 6,141 homes (443 ha)
- 9 hotels with 4,080 hotel rooms (721 ha) [the 22,503 number on the infographic below is an error]
- 2 golf courses and practice ground (162 ha)
- Services, infrastructure, maintenance (334 ha)
- 1 landing strip
- 1 14-km aqueduct
- Shops, convention center, etc

Infographic from www.cabopulmovivo.org Click to enlarge
According to the developers. Cabo Dorado “will be a fully integrated development, a first of its kind in the country, as it combines educational, recreational activities, scientific research, health promotional centers and a strong commitment to preserve the environment.” To this end, the project includes “an interpretation center, a technological and biological research center for studies related to the Sea of Cortes and the Desert of Baja California Sur, as well as a cultural exchange center, an educational institute and a student campus. In addition, there will be centers dedicated to the promotion of trade and investments, a high performance sports center, 9 world-class hotels and residences for temporary visitors and full time residents.”
Cabo Dorado will extract up to 4.8 million cubic meters of water a year from Santiago aquifer, roughly equivalent to the water needs of a city of 82,000 people) and will generate 711,900 kilograms of waste per day.
On the positive side, the project will create 18,000 direct and indirect jobs and bring around 900 million dollars/year into this area. It does not involve a marina or pumping wastewater into the sea which should prevent direct adverse ecological impact on marine life. The masterplan includes a “support town” for workers, which means that the local municipality does not need to build additional infrastructure to support the project.
The Mexican Center for Environmental Law (CEMDA) has called for a formal public meeting and consultation to ensure people are adequately informed about the latest plans and the potential social and environmental impacts.
Further reading:
For an exceptionally informative series of papers (in Spanish) on all aspects of tourism and sustainability in Cabo Pulmo, see Tourism and sustainability in Cabo Pulmo, published in 2008 (large pdf file).
Related posts: