In this post, we consider the unfortunate plight of the Tohono O’odham people, whose ancestral lands now lie on either side of the Mexico-USA border.
How did this happen?
Following Mexico’s War of Independence (1810-1821), the rush was on to draw an accurate map of all of Mexico’s territory. Mexico’s boundaries following independence were very different to today. At that time, the major flows of migrants linking the USA to Mexico were from the USA to Mexico, the reverse of the direction of more recent flows, where millions of Mexicans have migrated north.
As this map of Mexico in 1824 shows, Mexico’s territory extended well to the north of its present-day limits.
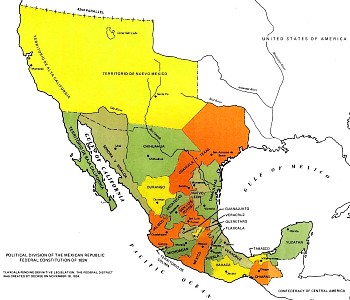
Map of Mexico, 1824
At the end of the Mexican-American War (1846-1848) the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ceded over half of Mexico’s territory to the USA. A few years later, under the 1853 Gadsden Purchase (Treaty of La Mesilla), northern portions of Sonora and Chihuahua (shaded brown on the map below) were transferred to the USA.
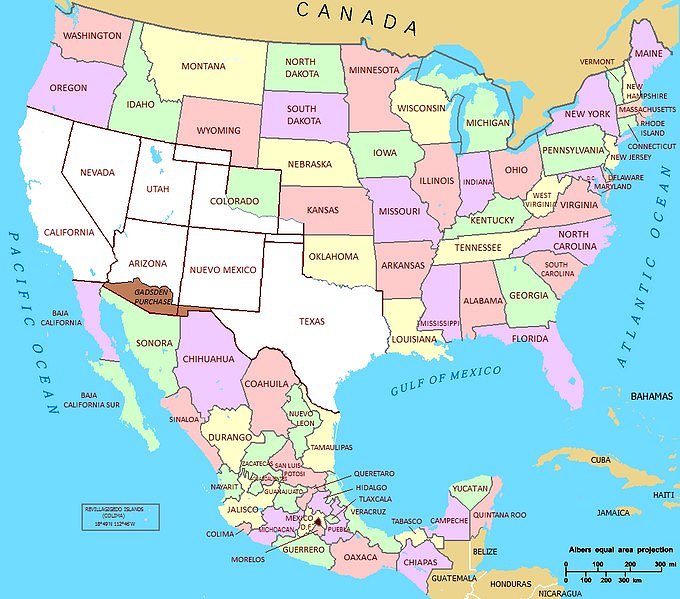
Source: National Atlas of the United States (public domain)
With minor exceptions since, to take account of changes in the meanders of the Río Bravo (Grande), this established the current border between the two countries.
Impacts on the Tohono O’odham people
One of the immediate impacts of the Gadsden purchase was to split the lands of the Tohono O’odham people into two parts: one in present-day Arizona and the other in the Mexican state of Sonora, divided by the international border. The O’odham who reside in Mexico are often known as Sonoran O’odham.
There are an estimated 25,000 Tohono O’odham living today. Most are in Arizona, but about 1500 live in northern Sonora. In contrast to First Nations (aboriginal) groups living on the USA-Canada border who were allowed dual citizenship, the Tohono O’odham were not granted this right. For decades, this did not really matter, since the two groups of Tohono O’odham kept in regular contact for work, religious ceremonies and festivals, crossing the border when needed without any problem. Stricter border controls introduced in the 1980s, and much tightened since, have greatly reduced the number of Tohono O’odham able to travel freely. This is a particular problem for the Tohono O’odham in Sonora, most of whom were born in Mexico but lack sufficient documentation to acquire a passport.

Tohono O’odham border protest
Since 2001, several attempts have been made in the USA to solve the “one people-two country” problem by granting U.S. citizenship to all registered members of the Tohono O’odham, regardless of their residence. So far, none has succeeded.
The largest community in the Tohono O’odham Nation (the Arizona section of Tohono O’odham lands) is Sells, which functions as the Nation’s capital. The Sonoran O’odham live in nine villages in Mexico, only five of which are offically recognized as O’odham by the Mexican government.
The border between the two areas is relatively unprotected compared to most other parts of the Mexico-USA border.
The Tohono O’odham Nation is often called upon to provide emergency assistance to undocumented workers (and drug traffickers) from south of the border who have underestimated the severe challenges of crossing this section of the harsh Sonora desert. Tribal officials regularly complain about the failure of the U.S. federal government to reimburse their expenses.
ABC News reports (Tohono O’odham Nation’s Harrowing Mexican-Border War) that the border “has made life a daily hell for a tribe of Native Americans” and that drug seizures on the Tohono O’odham Nation’s lands have increased sharply.
Want to read more?
- The Sonoran O’odham lieutenant governor continues to help after 16 years
- A story passed down from generation to generation (Lisa Palacios, a Tohono O’odham anthropology student at the University of Arizona with relatives on both sides of the border shares her grandparents’ story)