Tourism associated with rivers and lakes
So far as tourism is concerned, Lake Chapala is far more important than the other bodies of water within the basin. Only limited recreational activities are practiced in the various man-made reservoirs and in lakes Yuriria and Cuitzeo. Tourism is locally important in Zirahuén the most pristine of the basins lakes, but its small area restricts development prospects. Tourism, including ecotourism, is also locally important in Lake Pátzcuaro, with pronounced seasonal peaks corresponding to school vacations and the annual Night of the Dead. Surprisingly, there are no specialized ecotourism services at Lake Chapala.
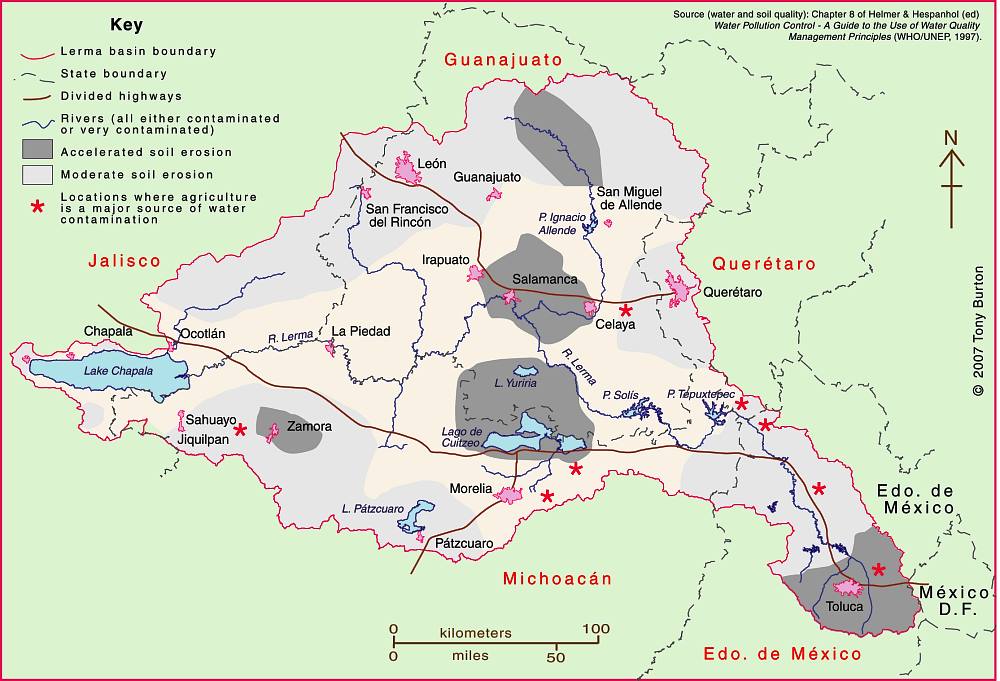
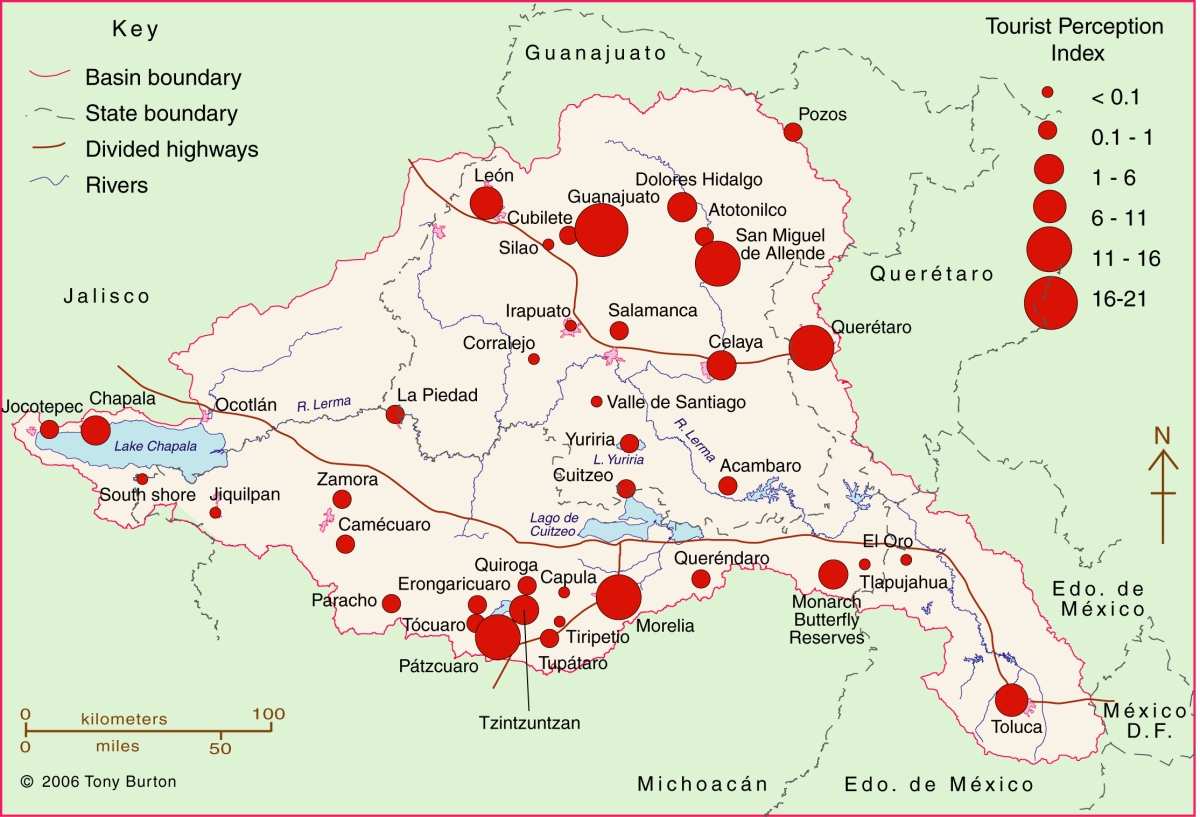
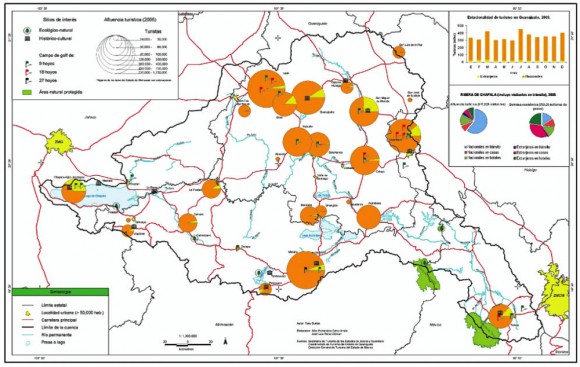
Lerma-Chapala Basin. Cartography: Tony Burton/Geo-Mexico; all rights reserved
The map shows areas of soil degradation in the Lerma-Chapala basin, as well as the locations where agriculture is a major source of water contamination. The environmental impacts of tourism in the basin are concentrated in the major cities such as Guanajuato, San Miguel de Allende and León, as well as in the smaller communities where tourism is of particular importance, such as Chapala and Pátzcuaro.
The lakes in the basin, especially Chapala, have always had more significance than the rivers for recreation and tourism activities. In the nineteenth century, sail canoes plied the waters of Lake Chapala. Fluctuating lake levels since the 1950s have prevented any concerted effort to establish modern water sports (yachting, water-skiing, windsurfing) on the lake, though casual users can be seen sporadically, mainly at weekends and during school holidays. Recreational fishing is virtually non-existent in the basin. Boatmen and fishermen often have conflicting demands.
Potential for ecotourism
Environmental degradation throughout the basin has reduced the number of potential ecotourism locations. The few remaining natural habitats are in urgent need of effective conservation. None of the few small areas of the basin currently protected at a federal level is associated directly with the River Lerma or Lake Chapala. Several tourism hot spots are under extreme pressure, operating at close to carrying capacity (defined as the maximum number of visitors they can handle without adverse environmental impacts). They include the Monarch butterfly reserves, Lake Camécuaro National Park, and the island of Janitzio in Lake Pátzcuaro. Well managed tourism could help finance habitat restoration and protection. Successful planning will require considerable local participation.
Lovers of flora and fauna want to see native and endemic species, rather than imported exotics. Bird-watching is one of the fastest growing recreational activities in the U.S., a huge niche tourism market in a wildlife watching industry worth 10 billion dollars in North America (Stap, 2002). In the basin, bird-watchers have the opportunity to see several endemics, as well as spectacular flocks of the White Pelican (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos), which can be better viewed on the relatively undeveloped southern shore of Lake Chapala than in its breeding grounds far to the north.
The development of horse-back riding, hiking and walking trails holds considerable potential for the future. Niche markets, such as cultural, shopping and eco-tours could all be further developed. Most tourists prefer a mix of experiences; the basin offers numerous, varied tourism possibilities.
Historically, hunting was an important activity in certain areas, particularly in the marshes at the eastern end of Lake Chapala (the ciénega). One ecological issue here, aside from any need to manage wildlife numbers, is the gradual decomposition of the lead-rich cartridges used a century ago. While this needs further study, this is gradually leaching lead into the environment, but is not the only source of the elevated levels of lead that have been reported in fish and lirio samples (Jay & Ford in Hansen & Van Afferden, 127). Careful monitoring is needed to ensure that no health risk is posed to humans.
Tourism exacerbates existing demands for limited supplies of water. This needs to be recognized in tourist-oriented cities such as San Miguel de Allende, Guanajuato and Pátzcuaro. Some recreational and tourism developments are more water demanding than others. Large expanses of grass cause high losses of water through evapo-transpiration especially during the dry season when watering is needed if grass is to be kept green. However, in the rainy season, grass promotes higher infiltration rates, enhancing groundwater recharge. Pressure from public and private gardens for water could be significantly reduced by xeriscaping.
Management is also needed to ensure that chemicals used in gardens, hotel grounds, and hotels do not cause pollution. The misuse of fertilizers and pesticides can have serious deleterious environmental effects. Overfertilization, for example, can increase nitrogen and phosphorus loads on watercourses, promoting eutrophication.
Golf can be one of the least environmentally sound of all recreational activities (Elkington & Hailes 1992). Constructing a golf course may involve habitat destruction and loss of wildlife; its maintenance may require copious quantities of water and agro-chemicals. A single course may use 330,000 cubic meters of water a year, as much as 4,500 people (Walsh, 2004) Aside from the ethical issue of whether water should be allocated to the playgrounds of the rich while the poor go without, golf courses can greatly reduce water consumption with careful design and management. Of Mexico’s 200+ golf courses, at least 23 are located in the basin. Several were built in the past twenty years. Several others are still in the planning stages. More golf courses may attract more retirees and tourists, but decision makers need to consider the possible social and environmental effects of constructing more courses.
References:
- Hansen, Anne M. & van Afferden, Manfred (ed). The Lerma-Lake Chapala Watershed: Evaluation and Management. New York: Kluwer Academic / Plenum Publishers. 2001.
- Elkington, John & Julia Hailes. Holidays that don’t cost the earth. The guide to greener holidays. London: Victor Gollancz Ltd. 1992.
- Stap, Don. “Great Florida Birding Trail” in Audubon Magazine September, 2002.
- Walsh, J. “War over water”. Golf Course News, October 2004. G.I.Media. 2004
Source:
This post is based on my contribution (on tourism) to the Atlas de la cuenca Lerma-Chapala, construyendo una visión conjunta, published by Semarnat-UNAM-IE, Mexico, in 2006. (The link is to a low-resolution pdf of the entire atlas).
Related posts: